Gas Nitriding of Titanium
Interest in solution gas nitriding and diffusion of nitrogen into the surface of titanium alloys as a means to inhibit adhesive wear (galling) while replacing heavier steel machinery parts has been increasing in applications involving moving components. The use of vacuum furnaces with partial pressure nitrogen atmospheres provides a practical and economical means for titanium nitride case hardening. The need to establish a consistent, quality process requires knowledge of the specific vacuum furnace used and the effect of partial pressure nitrogen, temperature, and time. The current study looks at the effect of partial pressure on the case hardness, depth, and surface chemistry of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. It is noted that this study is ongoing and more complete conclusions are planned to be published following further work.
Introduction
For all of the known benefits of using titanium alloys, including high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance, titanium unfortunately is known to exhibit poor tribological properties. That is, it has a high coefficient of friction (COF) when in moving contact with many mating materials, resulting in poor sliding and adhesive wear resistance that leads to failure by galling. Owing to this, metal-to-metal applications encountering friction and wear considerations require a surface treatment for adequate serviceability. This is increasingly a topic of investigation as various segments of industry are searching to reduce moving mass in machinery components (1, 2).
One treatment for enhancing the tribological properties of titanium that has been researched for years is nitriding, which is performed by plasma or gas processes (3). Nitrogen has great affinity and solid solubility in alpha titanium, which greatly increases hardness/strength (1, 3). Gas nitriding, which is the topic of this study, is classified as a diffusion process, whereby nitrogen gas dissociates and nascent nitrogen is adsorbed and diffused into the titanium matrix. This nitriding process is not a “coating”; it is a thermochemical heat treatment where nitrogen becomes an integral part of the titanium matrix. So unlike a coating, it does not have to initially bond well to function well; the case will not peel/flake away from the base metal.
The titanium/nitrogen phase diagram shows that higher levels of nitrogen will form compounds of titanium and nitrogen that can be thought of as a hard ceramic. Provided the compound layer is not too thick and depending on its chemical makeup and service application, it can provide greatly enhanced wear performance. Below the surface compound layer is a diffusion zone that is solid solution strengthened by nitrogen. This adds support to the surface for sustaining higher application loads, and like other diffusion processes, the depth of the diffusion zone is dependent on the time and pressure of the treatment.
Titanium has an even stronger affinity for oxygen than nitrogen, making the purity of the nitriding atmosphere highly influential to the end results (1, 3). Investigation into the formation of oxygen enriched surfaces (at high levels forming alpha case) in vacuum heat treating titanium using a graphite insulated vacuum furnace revealed that even at good commercial vacuum levels of 5 x 10-4 Torr, titanium became surface enriched with oxygen during heating to 1450°F (4) . The study of the “gettering effect” of titanium indicates that oxygen may be a constituent of the case structure when gas nitriding titanium in commercial vacuum furnaces. Depending on the amount present, oxygen in the nitride case is not necessarily a detriment. Oxygen interstitially strengthens titanium like nitrogen, and at a certain level may contribute to enhanced wear performance in a given application. Ti-6Al-4V has been purposely thermally oxidized to increase wear properties and reportedly performed comparatively well in a wear test study involving numerous surface engineering treatments (2).
Solar Atmospheres is developing processes for gas nitriding titanium in a vacuum furnace using partial pressure nitrogen gas at elevated temperatures. Of interest are the effects of partial pressure on the case hardness, case depth, and the surface chemistry/crystalline phases of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V.
Experimental Details
Ti-6Al-4V sheet was cut into approximately 1.5 inch squares. The surface of the coupons was used as received following a rigorous alcohol wipe; no surface blasting or polishing was performed prior to processing.
An all metal (molybdenum) vacuum furnace with a cylindrical, vertical hot zone, 10″ diameter x 18″ high, was used for this study. Three titanium coupons used for each run were hung on separate molybdenum wires attached to the lid of the furnace. All cycles began after an initial pump down to 2 x 10-5 Torr to assure vacuum integrity. The parts were heated in vacuum to 854°C (1570°F) and partial pressure nitrogen was introduced at 70 microns, 1 Torr (1000 microns), or 630 Torr. Nitriding time was 10 hours for each pressure.
Hardness profiles for each run were measured using a Struers Durascan and 25 gram load. Specimens were etched using 2% HF for metallographic analysis and total optical case depth measurement. The RJ Lee Group in Monroeville, PA performed surface analyses using x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and x-ray diffraction (XRD). The intent of this study was to determine the influence of pressure selection as a means to control the formation of TiN, Ti2N and Ti oxide.
Results and Discussion
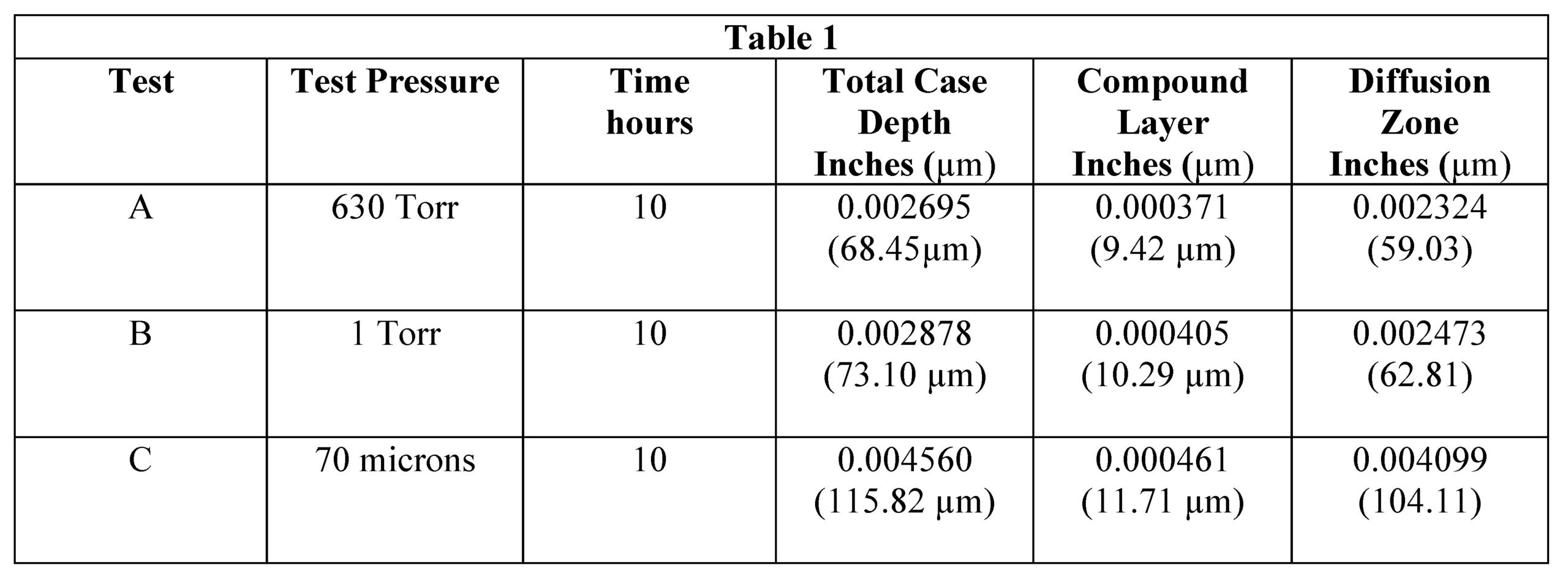
The hardness profiles for the three pressures evaluated are presented in Figure 1. This shows that the hardness of the diffusion zone drops off sharply for the 630 Torr (A) and 1Torr (B) nitrided specimens. The 70-micron (C) results are comparable to the near surface hardness (0.0005 inches [12.7 µm]) of the 630 Torr (A) results, but show a deeper, more gently sloping diffusion zone hardness. Note that the diamond indenter of the Durascan is too large for the very thin compound layers (10 µm range) to be accurately measured. (A nano-indenter hardness tester is needed and will be used in further study along with scratch hardness testing.)
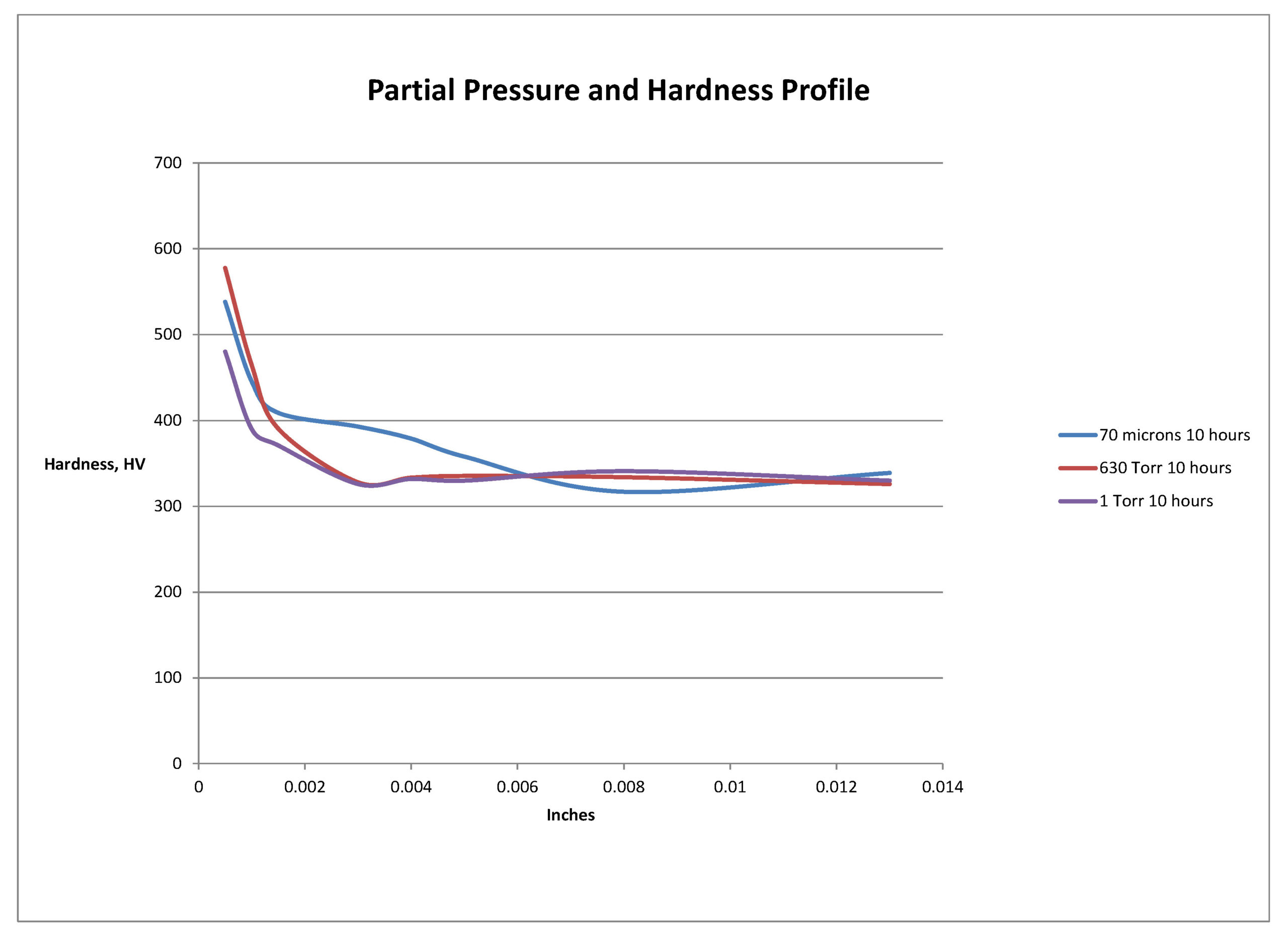
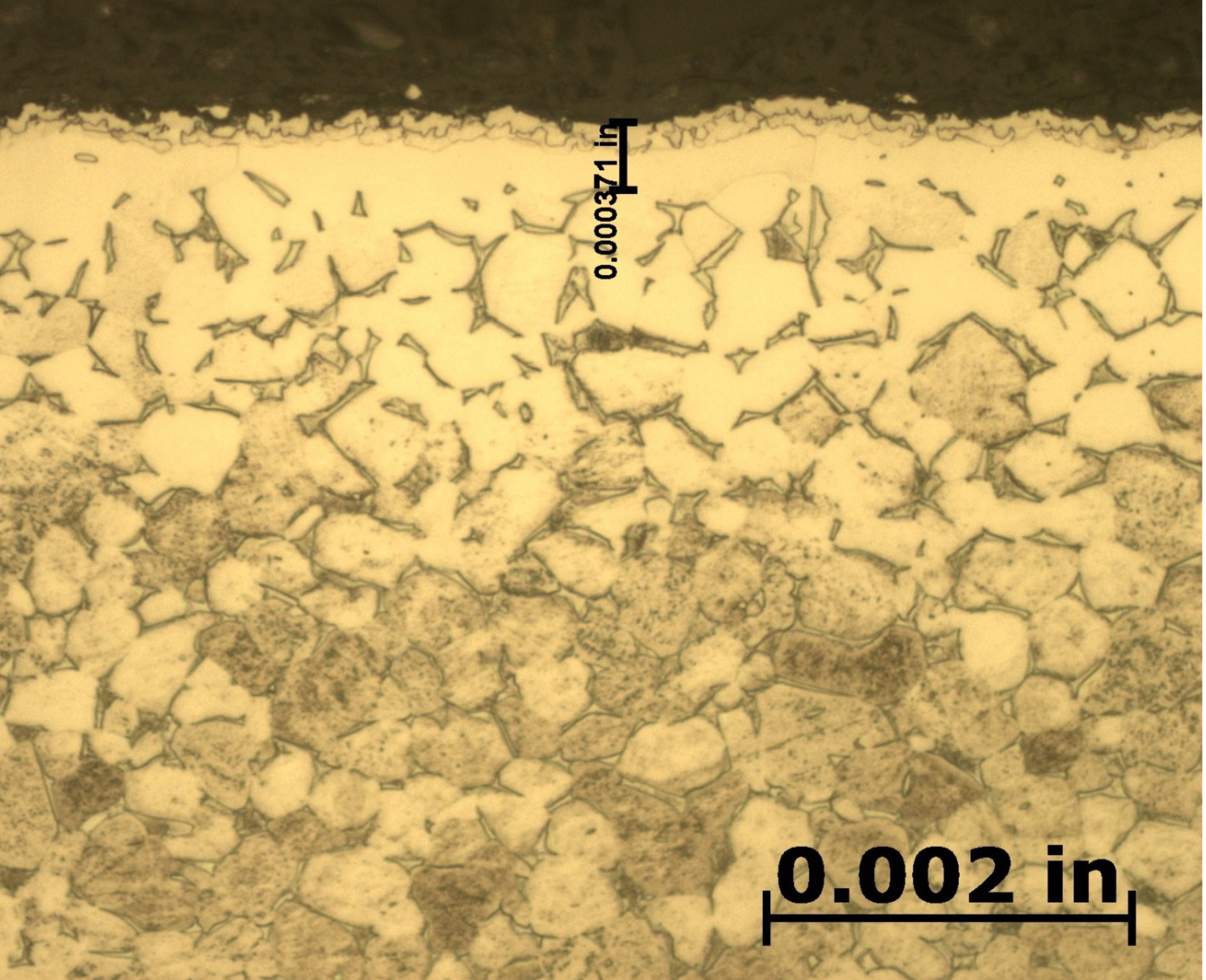
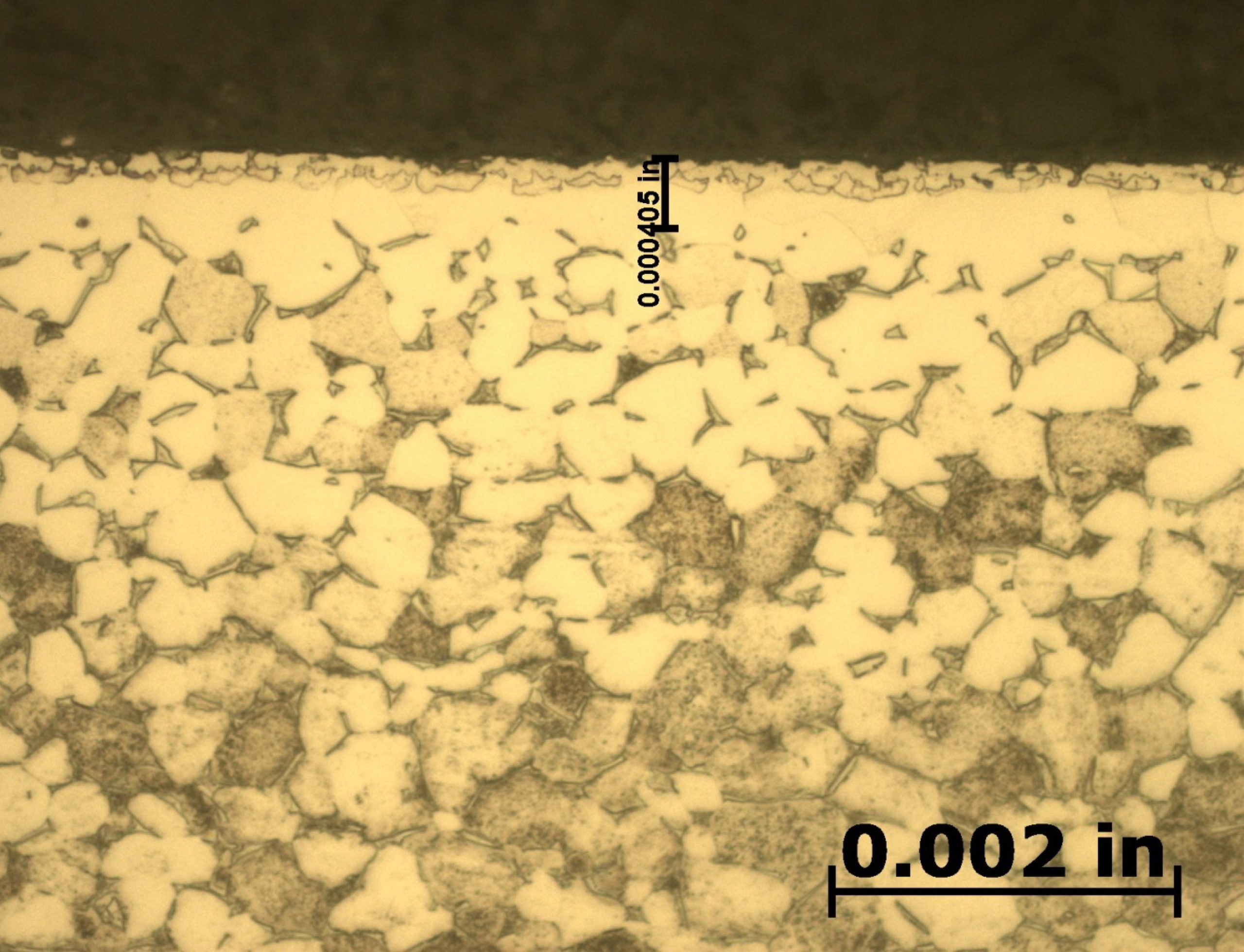
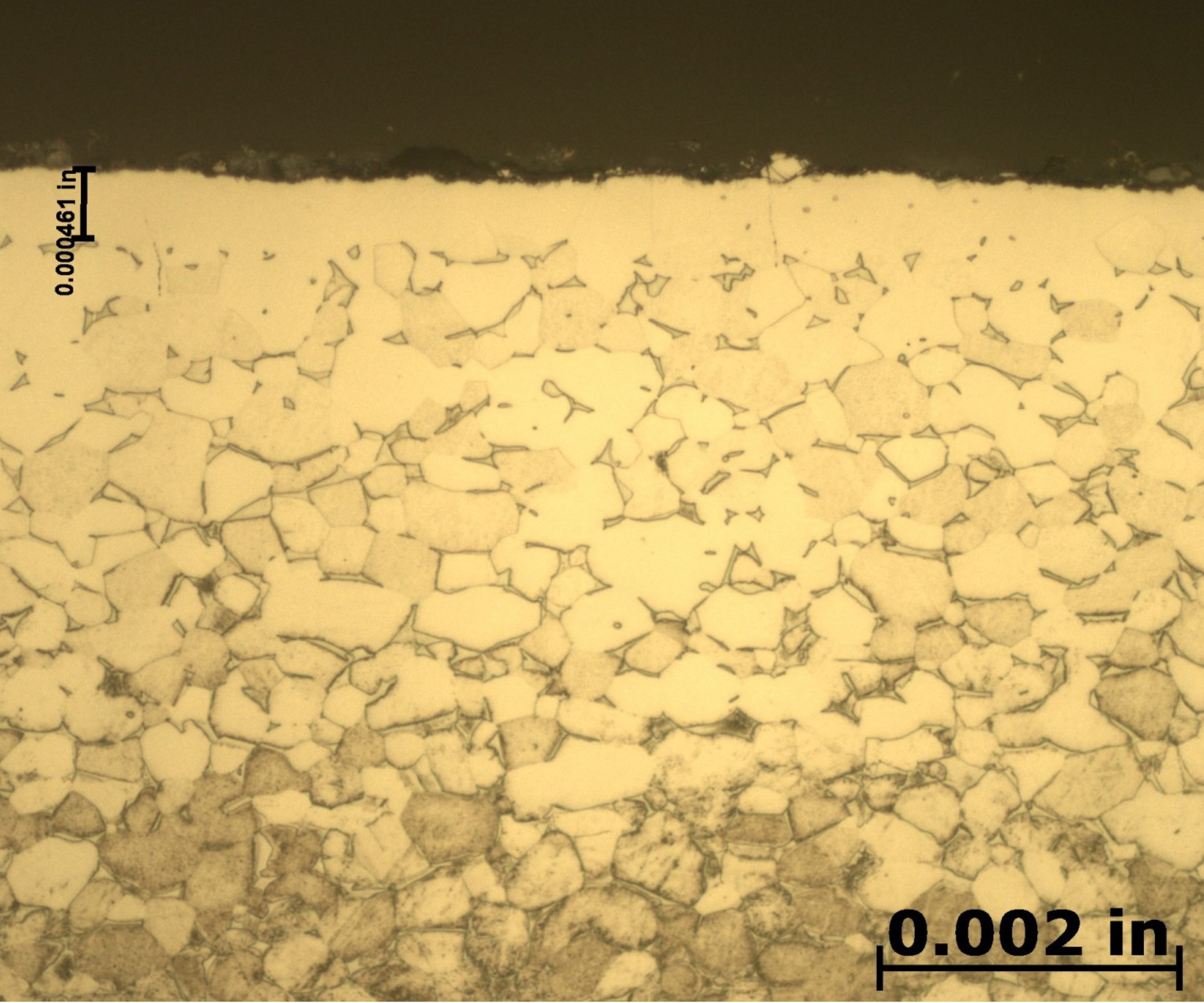
After etching to reveal the microstructure, optical measurements were performed for each pressure and the results are presented in Table 1. Tests A and B have comparable case depths while Test C has a case depth close to double the other two. The photomicrographs revealing the total case depths are shown in Figure 2. Higher magnification micrographs of Figure 3 show the thickness of the compound layer. The compound layer was comparable for all three pressures, yet the total case depth was deepest for the lowest pressure, corroborating the microhardness profile results.
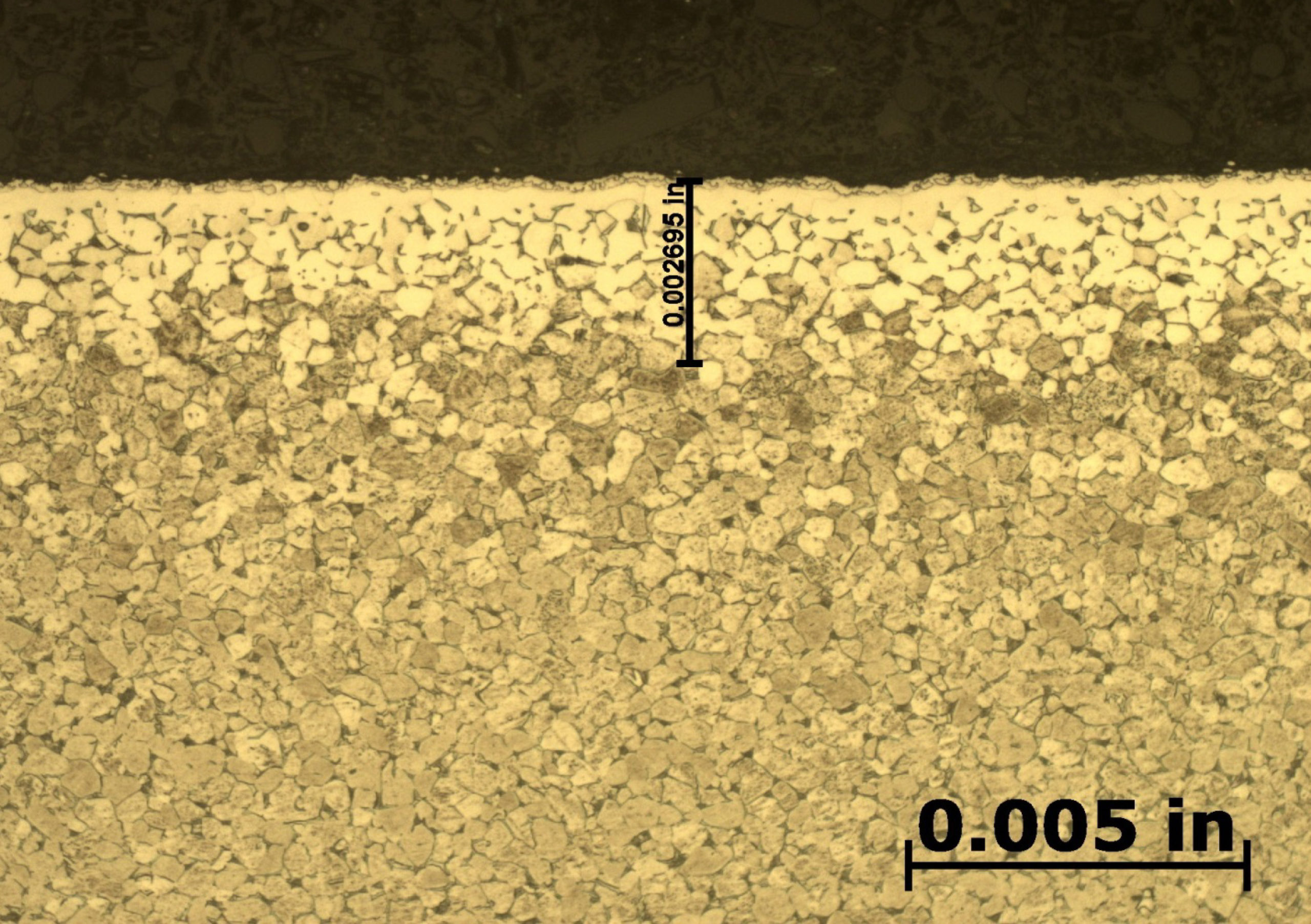
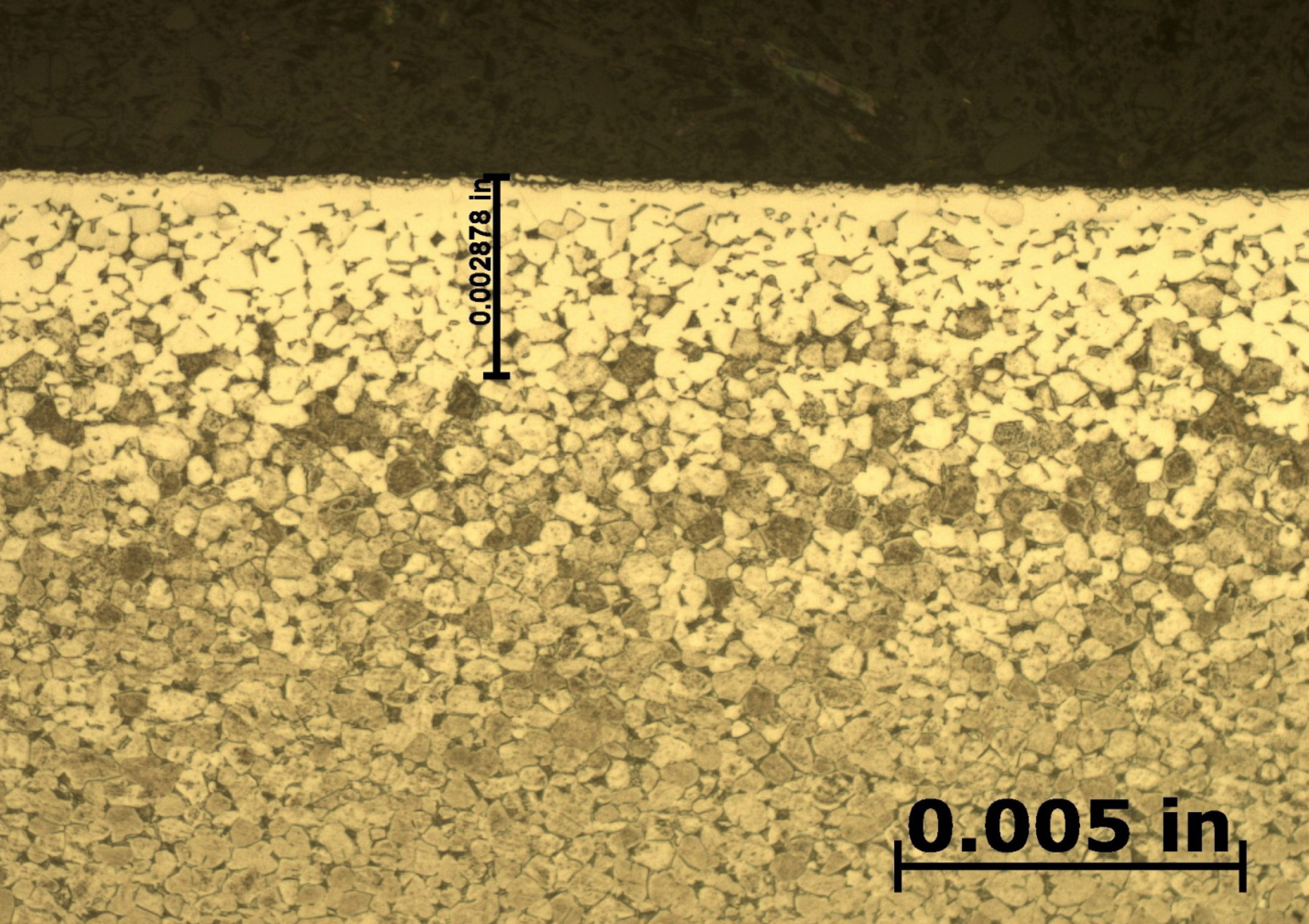
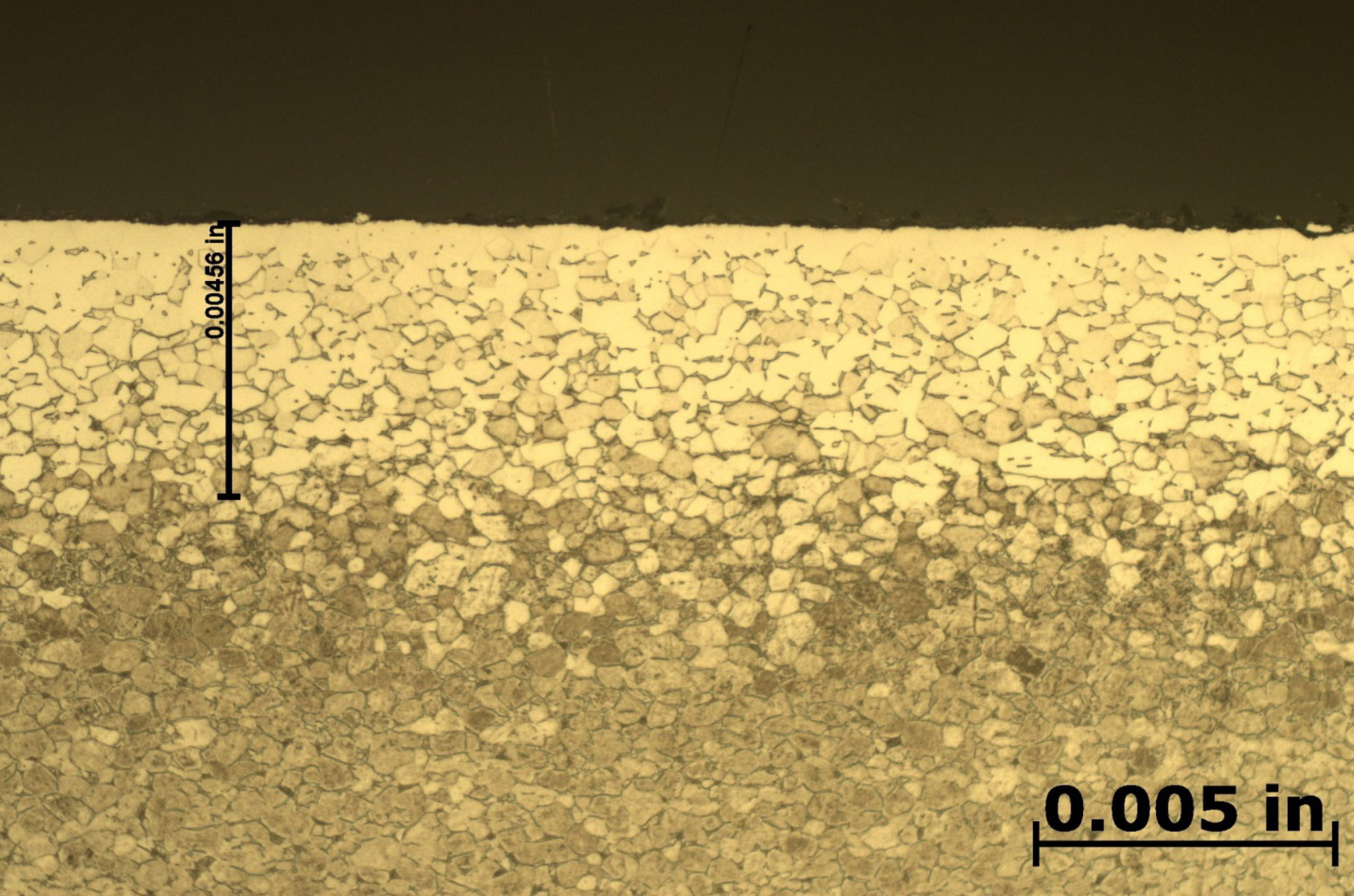
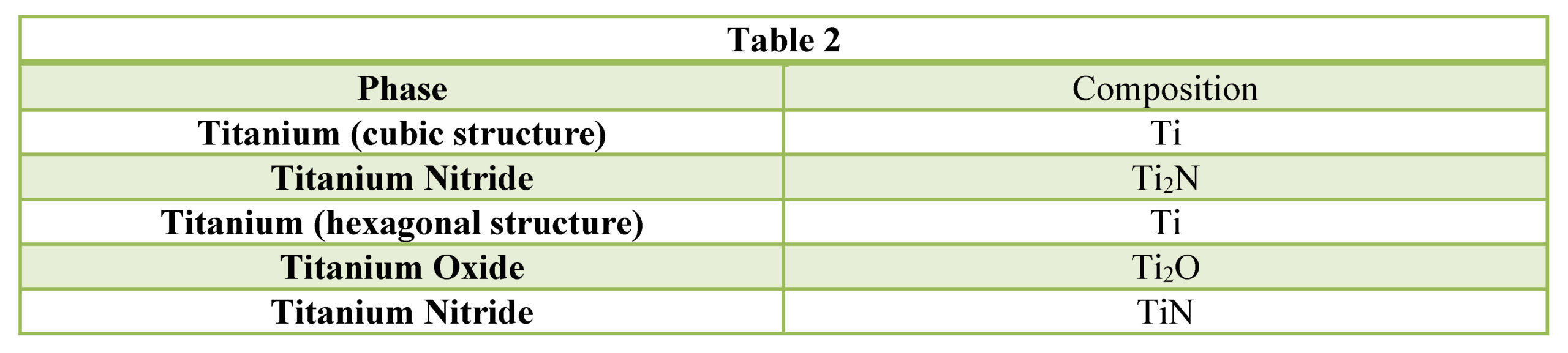
Based on prior investigations of the heat treatment of titanium alloys (4), it was surmised that the deeper case at the lowest pressure may be attributable to a higher presence of residual water vapor in the hot zone owing to a “stale atmosphere” (relatively poor quality vacuum). This would result in oxygen enrichment within the case when water vapor adsorbs and dissociates on the titanium surfaces. To confirm this hypothesis, surface analyses using x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and x-ray diffraction (XRD) were performed (5). The main crystalline phases detected with the XRD scans at each pressure are listed in Table 2. Oxygen is present on the surface as the titanium suboxide, Ti2O.
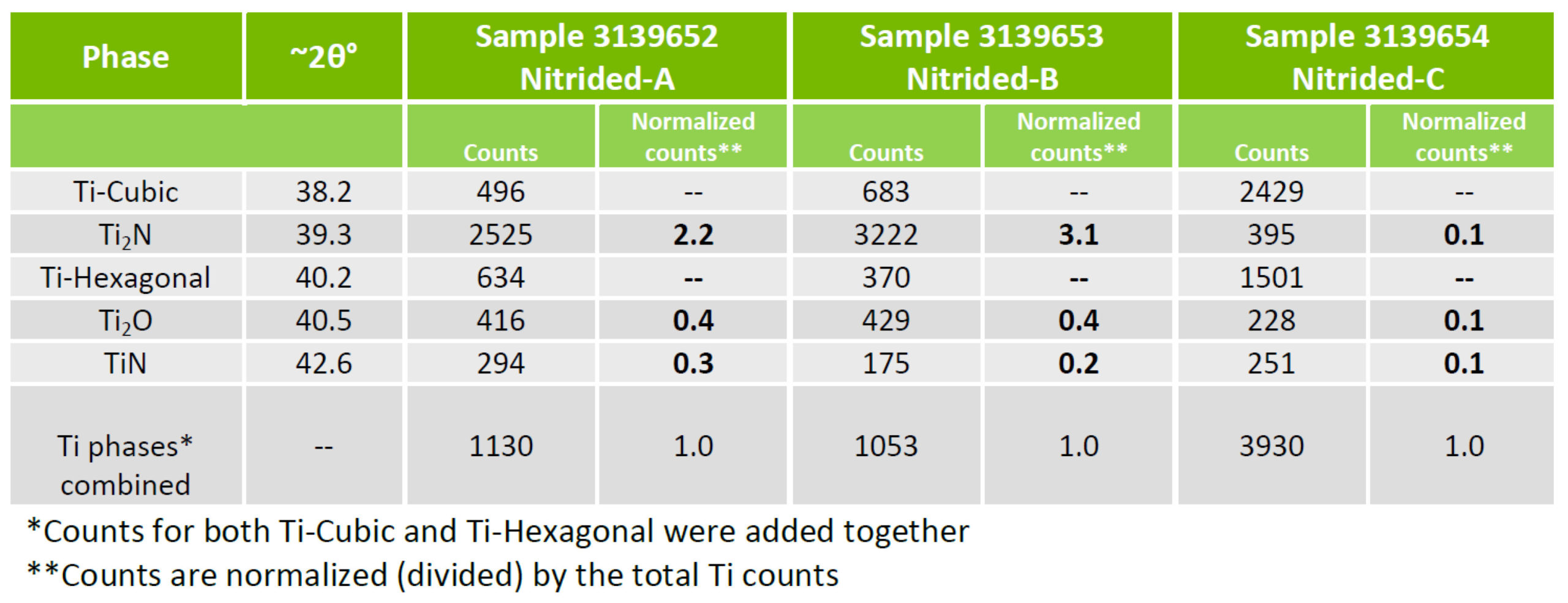
Normalized x-ray counts, Table 3, can be used determine the relative ratios of the compounds TiN, Ti2N and Ti2O. This reveals that the compound layer of Sample C, processed at the lowest pressure, has the highest oxide concentration, 33%, of the three samples. The oxide concentration of Sample A is 14% and 11% for Sample B.
Table 3
When processing at a low pressure of 70-microns, very little nitrogen flow is pumped through the furnace. Water vapor is inherently adsorbed in the hot zone insulation and thus the low nitrogen flow becomes concentrated with water vapor upon heating. Further, 70-micron flow results in low furnace volume turnover. This ultimately results in higher levels of oxygen in the case. This result supports the hypothesis.
Samples A (14%) and B (11%) oxygen concentrations are comparable owing to increased nitrogen pressures and gas flow rates resulting in greater dilution of water vapor by nitrogen. In order to maintain a pressure of 630 Torr (A), however, an almost completely closed vacuum at times leads to a decrease in the volume turnover at the highest pressure. This results in somewhat higher oxygen concentration at 630 Torr compared to 1 Torr.
Conclusions
This preliminary study revealed that the partial pressure of nitrogen when gas nitriding Ti-6Al-4V in a vacuum furnace can have a significant effect on the nitrided case characteristics. Processing with very low partial pressure of 70-microns resulted in a considerably higher amount of surface oxides being present in the compound layer compared to processing at higher pressures of 1 Torr and 630 Torr. The pressure and gas flow/turnover rate of nitrogen influences the “gettering ability” of titanium for oxygen during the nitriding process. The lowest pressure process resulted in a higher hardness profile and total case depth. This is considered attributable to oxygen being an interstitial strengthening element in titanium, just as it is nitrogen’s purpose in diffusion zone strengthening of the case.
At this point in the investigation it is unknown to what extent oxygen may enhance or detract from the wear performance of the nitrided case. Wear requirements for a product tend to be very application specific, but some standardized wear tests are planned for further study of vacuum nitrided Ti-6Al-4V. Reference (3) mentions nitriding of race car steering racks (rack and pinion gearing) as well as engine valves and spring retainers. Solar Atmospheres has nitrided titanium alloy engine valves and spring retainers, in addition to gears designed for the next Mars expedition land rover. This latter application is germane to the gear industry and the hope is that there is an increasing focus on reducing moving mass in machinery components, including gears.
Written by:
Virginia Osterman, PhD – Corporate Chemist, Solar Atmospheres Inc.
References:
- Bloyce, A., Morton P.H., Bell T.; Surface Engineering of Titanium and Titanium Alloys, ASM Handbook Volume 5, Materials Park, OH, 1994; 835-851.
- Bansal, D.G., Eryilmaz, O.L., Blau, P.J.; Surface Engineering to Improve the Durability of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Wear 271 (2011); 2006-2015.
- Rolinski, Ed; Nitriding of Titanium Alloys, ASM Handbook 4E, Materials Park, OH, 2016; 604-621.
- Jordan, D. and Osterman V.; Minimizing Alpha Case during Vacuum Furnace Heat treating, HTPro, Advanced Materials and Processes, March 2016; 46-48.
- RJ Le Group, XRD Analysis of Nitrided Titanium Report presented to Don Jordan, July 15, 2016.